Botox
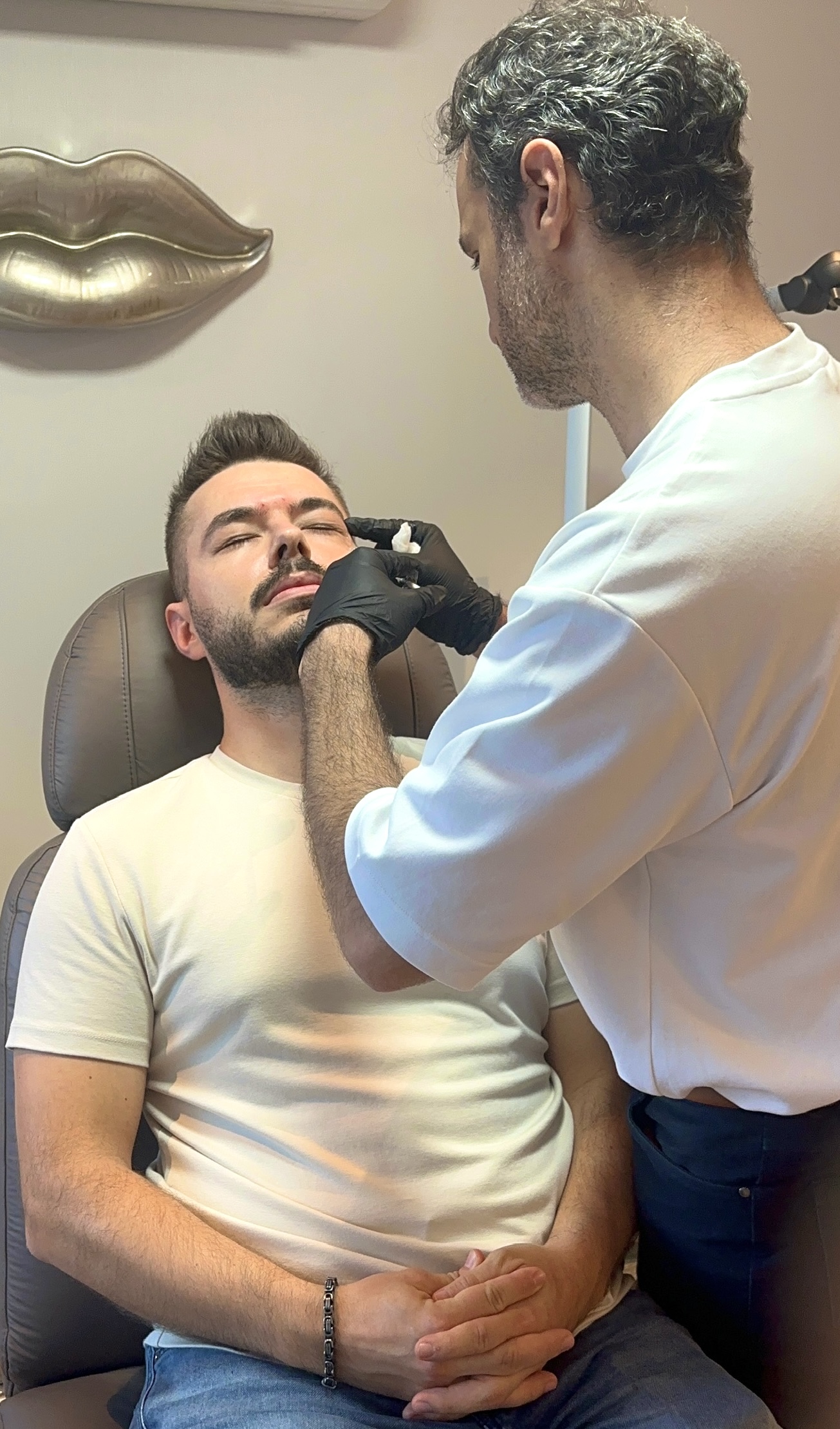
Botox is a brand name for a type of injectable cosmetic treatment that uses a purified form of the botulinum toxin to temporarily paralyze muscle activity. Botox is commonly used to reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines on the face, particularly in the forehead, between the eyebrows, and around the eyes (crow's feet).
Botox works by blocking the signals that are sent from the nerves to the muscles, preventing the muscles from contracting and causing wrinkles to form. The effects of Botox typically last for three to six months, after which the treatment can be repeated as needed.
-
Aesthetic Purposes: Botox is most commonly used to reduce wrinkles and restore a youthful and dynamic appearance to the face. It is particularly used to reduce fine lines on the face, such as forehead wrinkles, crow's feet (wrinkles around the eyes), and smile lines.
-
Medical Purposes: Botox is also used to treat certain medical conditions. For example:
- Migraine: In some patients with chronic migraine, Botox is used as an effective treatment to reduce migraine attacks.
- Bruxism and Temporomandibular Joint Disorders (TMD): In individuals who suffer from teeth grinding or clenching, Botox injections can be used to relax the jaw muscles and alleviate symptoms.
- Excessive Sweating (Hyperhidrosis): People with excessive sweating can receive Botox injections to deactivate sweat glands and reduce sweat production.
The Botox procedure is typically straightforward and is performed during a medical office visit, causing minimal discomfort for most people. However, the effects of Botox are temporary, and the treatment needs to be repeated every few months. Botox treatment should be administered by a medical professional, and a personalized treatment plan should be created. It is also important to be informed about the side effects of Botox and situations in which it might not be suitable. Consulting a doctor is always recommended.